Activities
Main activities
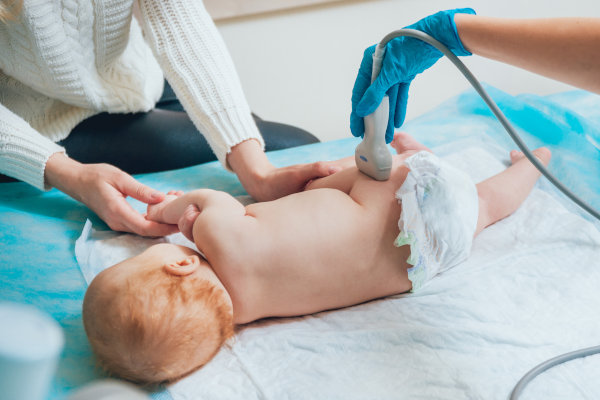
Hip luxation/Hip screening
According to new international recommendations, to screen for congenital hip dysplasia, all babies should have their hips examined by a paediatric orthopaedic specialist, preferably before 6 weeks of age. The physical examination is complemented by an ultrasound scan, which shows any problems with much greater precision. The examination is quick and painless. In the majority of cases, hip dysplasias detected early can be cured with timely treatment (e.g. Pavlik's harness).
More
Clubfoot
Congenital clubfoot is treated with the so-called Ponseti’s method, preferably starting from 3-4 weeks of age. The method involves the elongation of the Achilles tendon under local anaesthesia following serial casting and the use of a suitable orthosis. We do not put on casts in private clinic, but it is possible to have a consultation in a relaxed environment (even during pregnancy) before the treatment and a follow-up examination after the casts.
More
Other Activities
Flatfoot
A hosszanti lábboltozat süllyedését nevezzük lúdtalpnak, vagy bokasüllyedésnek. A láb vizsgálatát követően életmódbeli, cipő és cipőbetét viselési tanácsadás történik.Decrease of the longitudinal arch of the foot is called flatfoot. After the examination of the foot, recommendation is given concerning the lifestyle, shoes and shoe soles.
Hyperkyphosis
A postural defect common in childhood and adolescence, which can be corrected with a proper lifestyle and back and abdominal muscle strengthening.
Legg-Calve-Perthes’ disease
Perthes’ disease is the necrosis of the femoral head in childhood. Most common symptoms are intermittent thigh or knee pain. The duration of the disease is 3-5 years, during which regular orthopaedic follow ups are recommended. The conservative treatment is important. Surgery is recommended only rarely.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
It is the disease of the teenage, which is caused by the imbalance between the sexual and growth hormone levels. The slippage of the femoral head from the femoral neck requires urgent surgical intervention.
Torticollis
Due to the shortening of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, the baby prefers keeping the head turning only on one side. In long term facial asymmetry can develop. Most of the cases can be treated by physiotherapy. In more severe cases surgery is recommended.
Neuromuscular problems (muscle weakness, oxygen deficiency)
The most common neuromuscular problem is the cerebral palsy. The severity of the disease varies from patient to patient. Some has only a slight difficulty in walking, while others are mentally and somatically completely retarded. Their orthopaedic treatment contains different surgeries, tendon lengthening, bony surgeries, orthotic support, Botox injection and casting.
X-leg, O-leg, leg length discrepancy
Most of the axial deformities in childhood correct spontaneously. In more severe cases good correction can be achieved with a small surgical intervention (temporary growth stop). The same method can also be applied to correct leg length discrepancies.

